The strategic management process is a sequence of components indicating a definite step by step chronology. It is a standard sequence of four phases divided into total seven components or elements.
Strategic Management Process
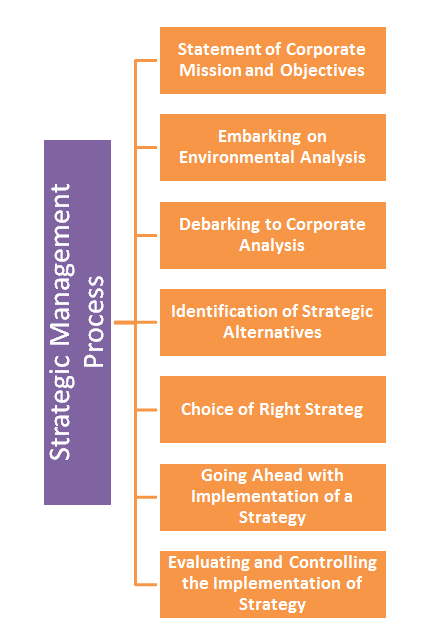
(1) Statement of Corporate Mission and Objectives – No human activity is unintentional. There is some objective behind his activities or creations-good or bad for what is good for one may not be good for another necessarily. Organisations are the deliberate creations of human beings having a definite mission towards which all efforts, energies, and resources are directed.
A mission is a fundamental and a unique purpose by which it becomes outstanding or distinct from another. The scope of its function is identified in its operation in product and market forms. A mission is long lasting making its intentions clear. It reflects the very philosophy of a decision maker. It is the image the organisation wants to imprint on everybody who comes in contact with it. A mission is the hub around which all managerial functions revolve. In the light of the mission-the main stay-company has objectives to attain or results are to be attained.
Compared to ‘mission’ the ‘objectives’ are of lesser value in that they can not be repugnant to the basic mission. Goods are the aims or destinations or direction in which the corporate is to move.
(2) Embarking on Environmental Analysis – Once the mission is clear, the objectives are stated the attainment of which is not that easy. To plunge in the race, there is need for understanding that environment. Every organisation is a sub-system which works as a part of supra-system namely environment made up of different external forces namely, social, cultural, legal, technological, ecological psychological and physical which are constantly changing themselves and influencing the entire environment. An organisation being part of this environment is subject to influence of different variables and influence the environment. Any interaction is an attempt to adjust itself with the environment. These environmental forces are uncontrollable by the organisation and only action is interaction of adjusting to the flowing currents. In interacting every firm is exposed to opportunities backed by threats also.
(3) Debarking to Corporate Analysis – As said earlier, external environment releases opportunities studded with threats and the extent the company encashes on this will depend on its ability that is its internal strengths and weaknesses. It is corporate analysis which touches the measurement of these company’s strengths and weaknesses. Internal strengths will help to overcome the weaknesses if they are gauged in proper perspectives. This internal analysis of strengths and weaknesses will also determine its ability to adjust to external environment. A wise man will look before he leaps. He does not take a blind chance simply as he is to leap.
(4) Identification of Strategic Alternatives – As the organisation is interacting with its external environment knowing its internal strengths and the weaknesses, stands to find opportunities and threats which have strategic alternatives. This exercise of exposing it to external environment and keeping updated of its strengths and weaknesses will render itself more bolder and shaper to dense and develop more alternatives.
It is like a “nine point puzzle” where you generate more and more alternatives of joining all nine points without lifting your pen from the paper and without duplicate the routes. Resultantly, the manager is to choose between or among the alternatives as to which is the best suited its internal strengths and weaknesses. There is need for choosing the strategic alternative; one which is the best filling in the framework of company mission, objectives on one hand and strengths and weaknesses on the other.
(5) Choice of Right Strategy – Once the alternatives are available, there is need for right strategy to tackle the situation. Strategy formulation is the result of making strategic decisions taking into account all the factors that determine or govern a given strategy. A given strategy is sure to influence organisation’s operation or working in any predetermined manner, the process of choice scientifically takes note of how each alternative strategy affects the variant critical factors that determine company’s working.
Again, a chosen alternative should be acceptable in the backdrop of company’s objectives. One should not jump to the conclusion that critically chosen strategy is the best one. It is because, in addition to environmental and organisational forces, there are some personal factors because choice of strategy is done by individuals who have their own personal value judgements and aspirations too. Though a manager, strategist is to be objective and open minded, there is a tendency to be subjective to a certain extent.
(6) Going Ahead with Implementation of a Strategy – Once the strategists finalise the strategy and has the approval by the higher ups, this dream is to be translated into a reality; a promise should result in performance without any gap. It is time to put the strategy into gear and seeing that strategy is put to action. It is because, the soundest strategy has no meaning unless, it is put to bring the expected result. However, implementation of strategy is not a child’s play. It calls for designing the suitable organisational structure, able and effective leadership, development of functional or operational policies, developing and allocating the resources, design of effective information system and structuring the control system for monitoring and so on.
(7) Evaluating and Controlling the Implementation of Strategy – This is the terminal stage of strategic management process. However, as business is on going activity, this function of control never ends. It is more a futuristic function that control and monitoring belong to. Continuous monitoring of the implementation of a strategy is a must so that corrective action can be taken if need there be. The variations between what is expected and actually happening, are measured, causes are traced and corrective action can be taken to put the strategy on the path of progress. These variations are likely to be the areas of choice of strategy, change in the mission and objectives or change in organisational structure. As change is another name for business, strategic business management is a dynamic process.
This strategic business management process brings to light certain implications. These implications are –
- The elements that make this strategic process are occurring in a definite sequence. Each step is logical.
- These elements are not independent but inter dependent or interrelated.
- To keep the strategic process on going, there is need for feed-back and
- The strategic management process is dynamic because variables are interrelated. This portion of the process of strategic managements has explained as to how to do it ?


Leave a Comment